Introduction
In today's rapidly advancing digital landscape, industries are increasingly leveraging emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) to streamline operations, reduce costs, and boost productivity. One of the most effective applications of these technologies is in Asset Performance Management (APM), where AI and IoT have transformed traditional approaches, allowing businesses to optimize their assets' performance, minimise downtime, and maximise return on investment.
In this detailed guide, we will cover everything you need to know about AI and IoT-enabled APM software. We will explore its components, the key financial benefits it offers, how it can be implemented, and real-world use cases. This blog will give you a complete understanding of how this technology can transform asset management practices across various industries.
What is Asset Performance Management (APM)?
Asset Performance Management (APM) is the process of monitoring, analyzing, and optimising the performance of physical assets such as machinery, equipment, and infrastructure. APM systems aim to improve the availability, reliability, and efficiency of assets while minimising maintenance costs and unplanned downtime.
Traditionally, APM relied on preventive and reactive maintenance strategies, where assets were serviced based on fixed schedules or after a failure occurred. However, with AI and IoT integration, APM has evolved into a more advanced, data-driven system that enables predictive maintenance and prescriptive and offers significant improvements in operational efficiency.
How AI and IoT are Transforming APM
The combination of AI and IoT enables more intelligent and proactive management of assets. Here's how each technology plays a role in modern APM systems:
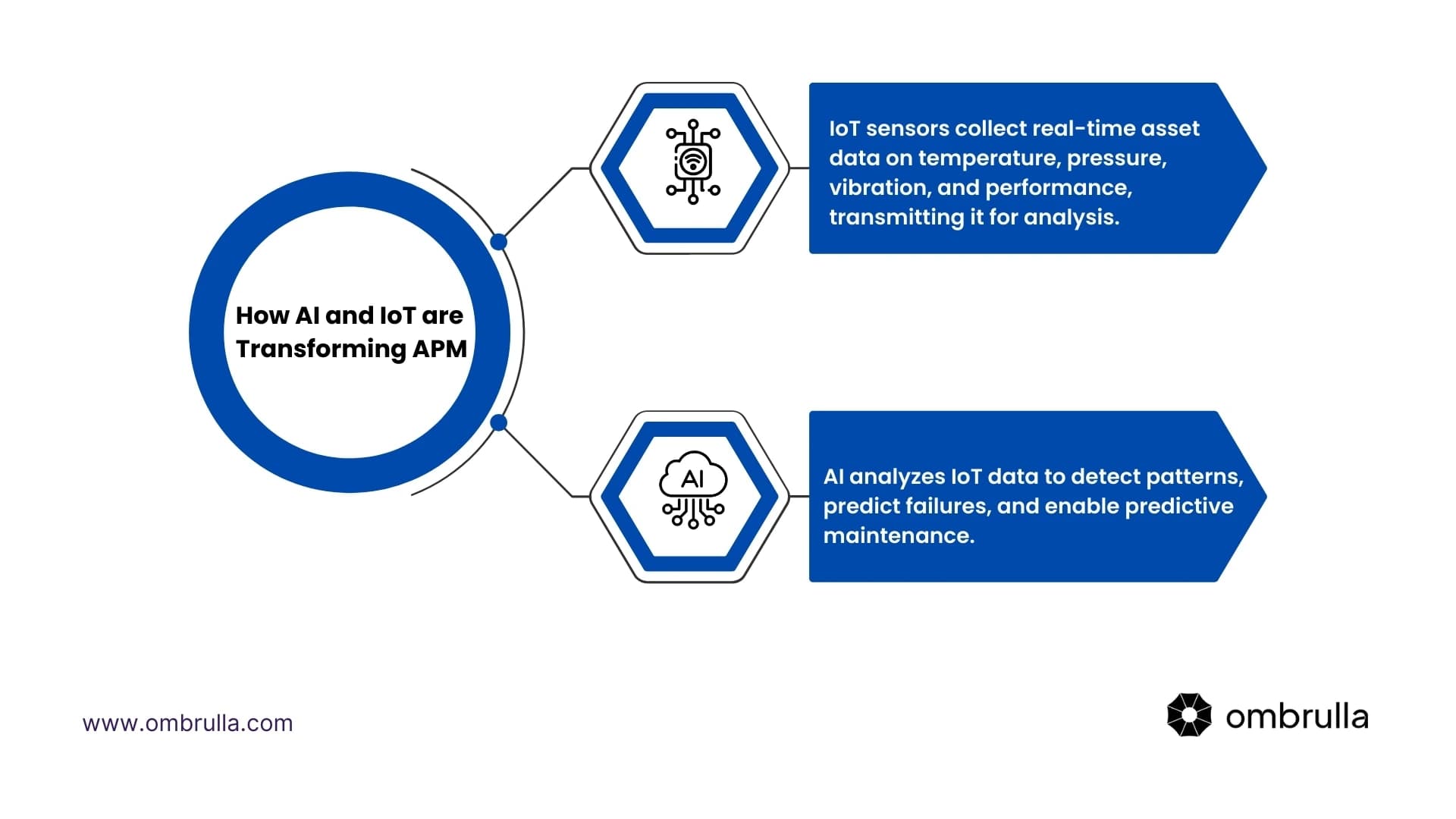
The integration of AI and IoT also enables prescriptive maintenance, where the system not only predicts when maintenance is needed but also provides specific recommendations on how to address the issue and optimise asset performance.
Key Components of AI and IoT-Enabled APM Software
To fully leverage AI and IoT in Asset Performance Management, the software typically includes key components like asset lifecycle management, predictive maintenance, and real-time data analytics. These help optimise overall equipment effectiveness and streamline operations.
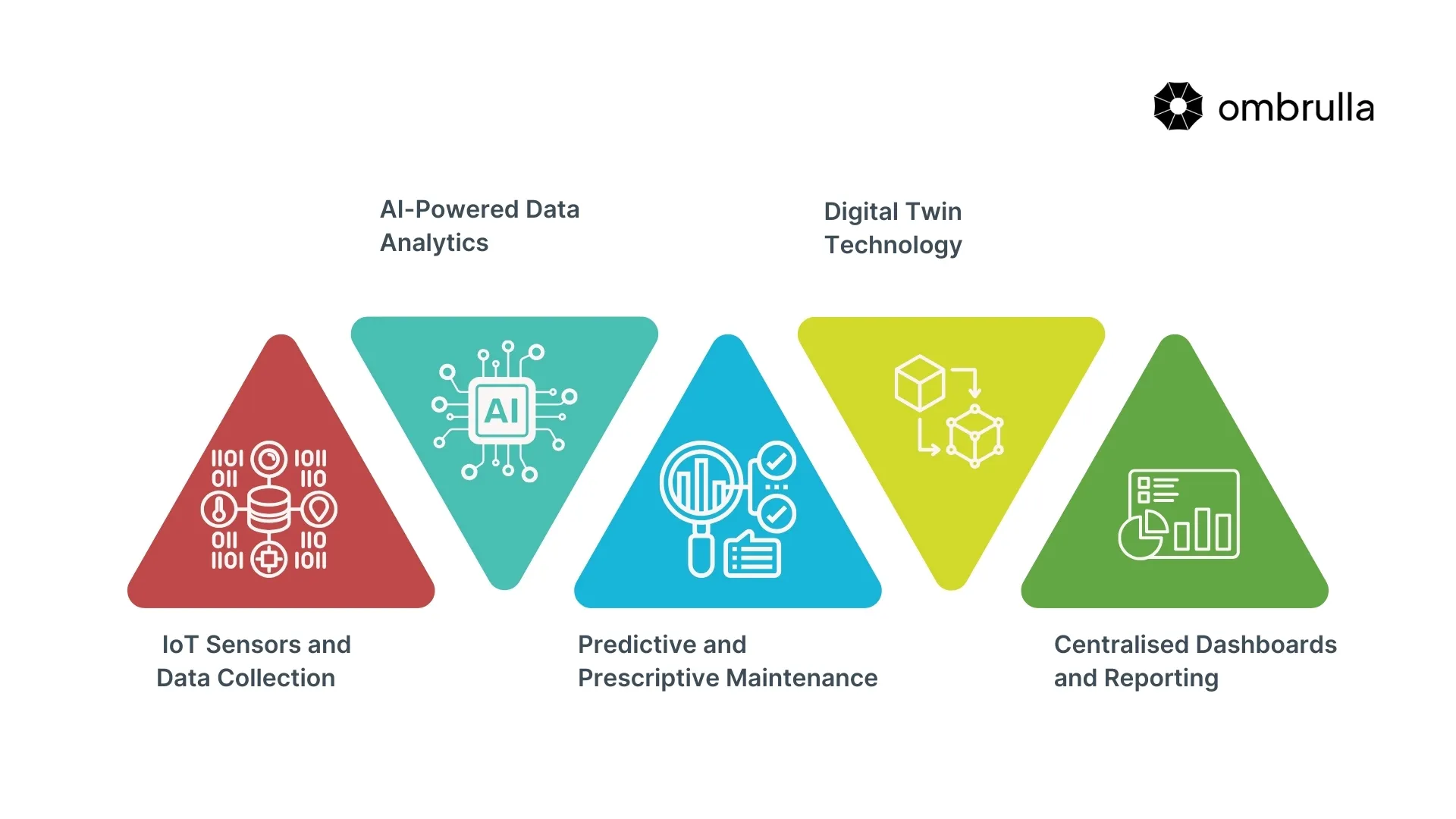
IoT Sensors and Data Collection
IoT sensors are installed on key assets to continuously monitor their condition and performance. These sensors capture critical data points such as:
Temperature
Vibration
Humidity
Operational speed
Pressure levels
Energy consumption
This real-time data provides valuable insights into the asset's health, allowing organisations to detect anomalies before they lead to failures.
AI-Powered Data Analytics
AI algorithms analyse the data collected by IoT devices to identify patterns and correlations. These algorithms use historical and real-time data to create models that can predict when an asset might fail, enabling predictive maintenance. Over time, AI models become more accurate as they learn from new data.
Predictive and Prescriptive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance helps organisations anticipate asset failures and perform maintenance activities at the right time, reducing unplanned downtime. Prescriptive maintenance takes it a step further by recommending specific actions to optimise performance, such as adjusting operational settings or replacing parts.
Digital Twin Technology
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical assets that simulate their behaviour in real-time. AI and IoT-enabled APM platforms often use digital twin technology to model assets operations, allowing businesses to test scenarios, forecast performance, and make data-driven decisions.
Centralised Dashboards and Reporting
APM software consolidates data from all assets into a single platform, providing a holistic view of asset health and performance. Centralised dashboards allow users to monitor asset conditions in real-time, generate reports, and set up alerts for specific performance thresholds.
Financial Benefits of AI and IoT-Enabled Asset Performance Management
The financial advantages of implementing AI and IoT-enabled APM software are substantial. Let's break down some of the key financial benefits:
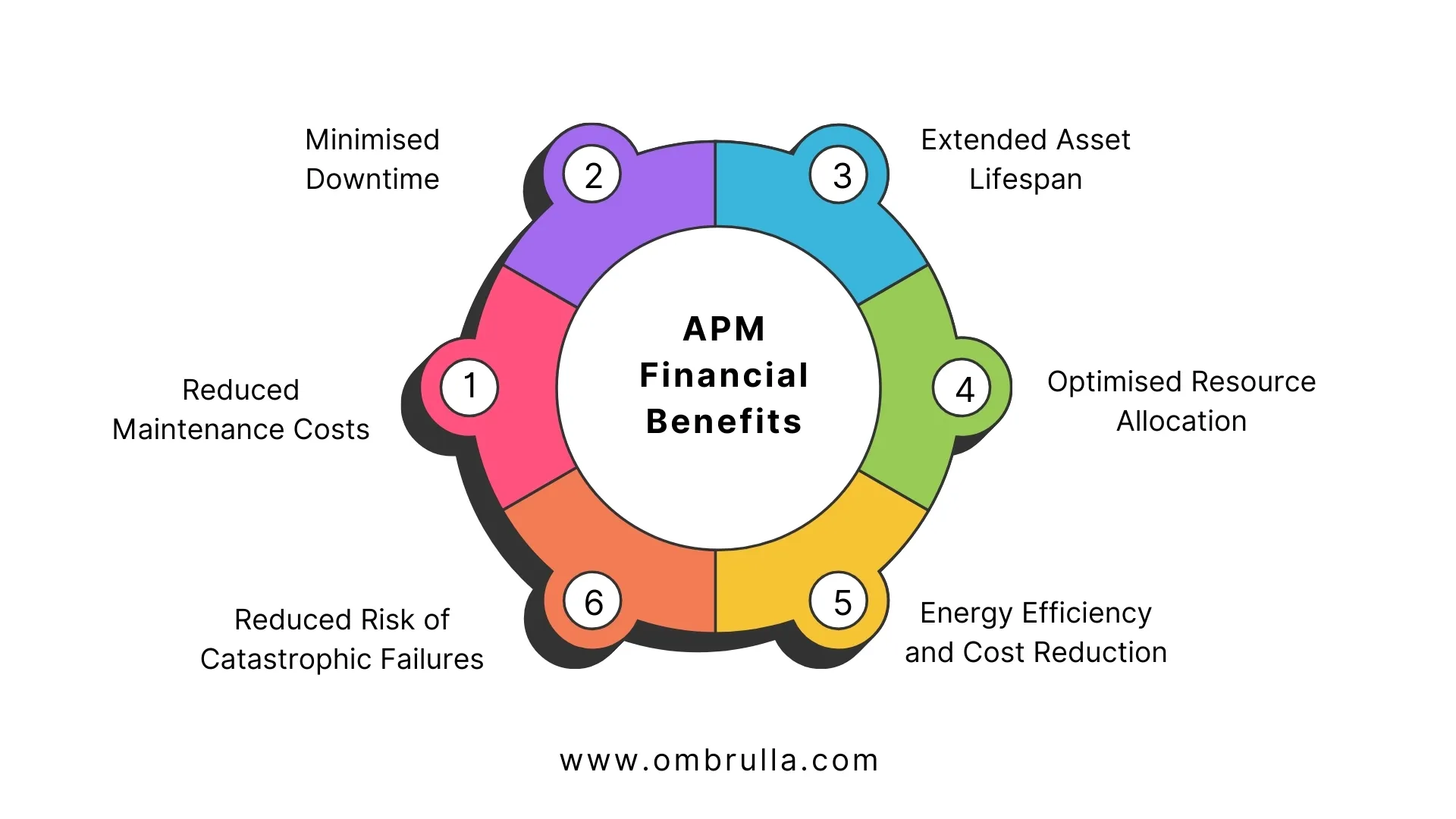
Reduced Maintenance Costs
One of the most significant financial benefits of AI and IoT-enabled APM software is the reduction in maintenance costs. Traditional preventive maintenance often leads to over-maintenance, where assets are serviced more frequently than necessary. On the other hand, reactive maintenance is costly because it requires emergency repairs and can result in extended downtime.
Predictive maintenance, enabled by AI, ensures that assets are serviced only when needed, minimising unnecessary maintenance activities and associated costs. By performing maintenance just in time, businesses can save on labour, parts, and service expenses.
Minimised Downtime
Unplanned downtime is one of the most expensive operational challenges for asset-intensive industries. For example, in the manufacturing industry, even a few hours of downtime can result in significant revenue losses.
AI and IoT-enabled APM systems predict when failures are likely to occur, allowing organisations to schedule maintenance during planned downtime rather than reacting to unexpected failures. This leads to higher asset availability and less operational disruption.
Extended Asset Lifespan
By continuously monitoring the condition of assets and performing timely maintenance, organisations can extend the operational life of their equipment. AI-powered APM software helps identify early signs of wear and tear, enabling businesses to replace parts before they cause major damage. This proactive approach reduces the need for costly asset replacements and maximises the return on investment (ROI) from capital assets.
Optimised Resource Allocation
AI-driven insights from APM software allow businesses to allocate resources more effectively. For example, by knowing which assets require maintenance and when, companies can avoid over-allocating labour or parts for unnecessary maintenance tasks. This leads to more efficient use of workforce and materials, driving cost savings.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Many APM systems also monitor energy consumption and emissions from assets. By optimising asset performance, organisations can reduce energy usage, leading to lower utility bills. In industries with energy-intensive operations, this can translate to substantial savings.
Reduced Risk of Catastrophic Failures
The cost of a catastrophic asset failure can be astronomical, not only in terms of repairs but also in terms of lost production, reputational damage, and potential safety risks. AI and IoT-enabled APM systems help mitigate this risk by providing early warnings and enabling proactive maintenance. By preventing major failures, organisations can avoid the significant financial and operational consequences that come with them.
Implementation Process of AI and IoT-Enabled APM Software
Implementing AI and IoT-enabled APM software requires careful planning and execution. This process involves integrating IoT predictive maintenance and leveraging APM solutions for optimal results. Follow this step-by-step guide to streamline asset performance management and enhance operational efficiency.
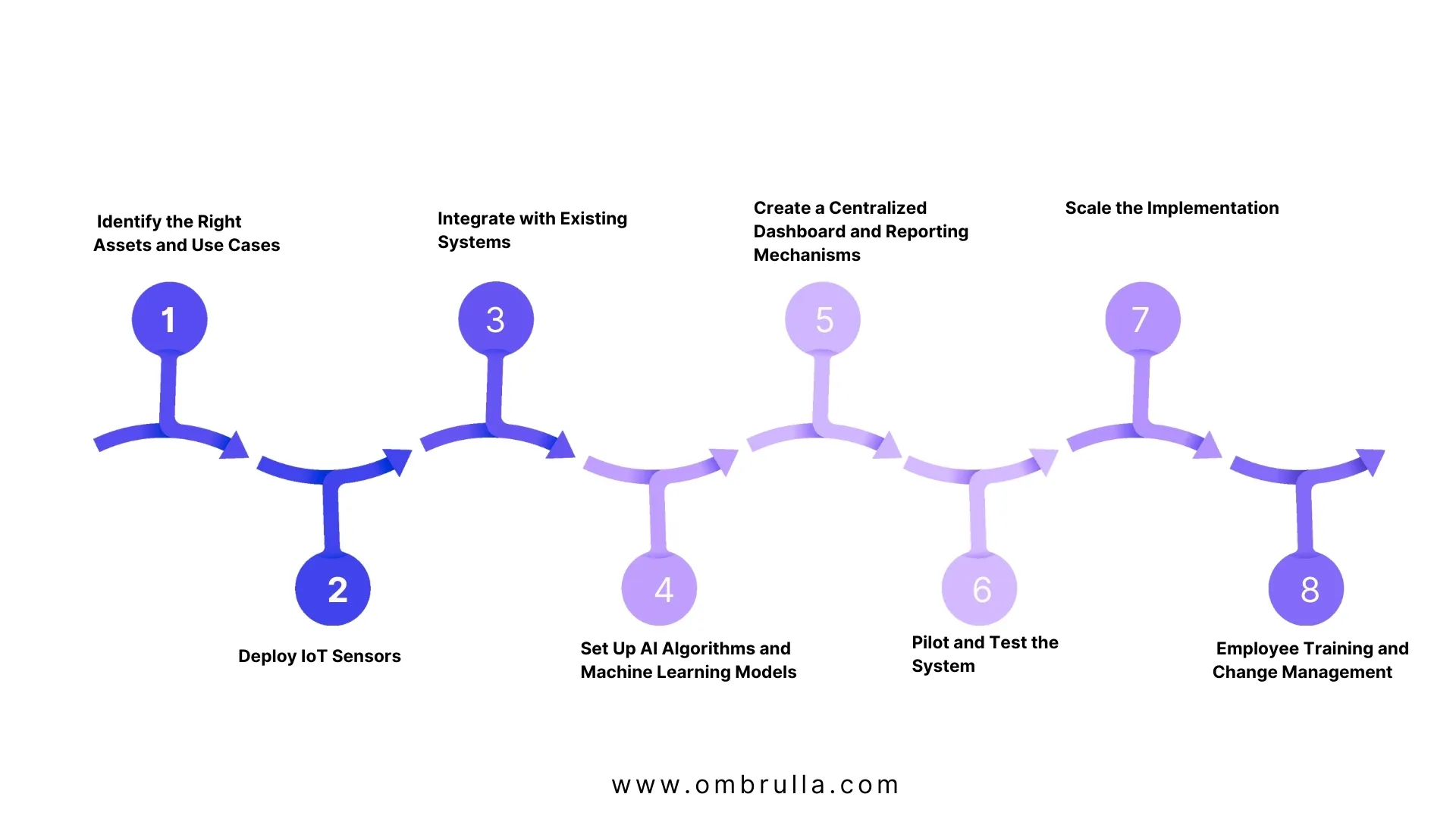
Identify the Right Assets and Use Cases
Before implementing APM software, it is crucial to identify the assets that will benefit the most from AI and IoT integration. Start with high-value, critical assets that have a significant impact on operational performance or incur high maintenance costs.
Next, define the use cases for the APM system. Common use cases include predictive maintenance, performance optimization, and energy efficiency. Clearly defining use cases will help guide the implementation process and set measurable goals.
Deploy IoT Sensors
Once the assets are identified, IoT sensors must be installed to collect real-time data. The type of sensor used will depend on the asset and the specific parameters being monitored (e.g., vibration, temperature, pressure). IoT devices must be strategically placed to ensure comprehensive coverage and accurate data collection.
Integrate with Existing Systems
APM software often needs to be integrated with existing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, Computerised Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS), or other asset management platforms. This integration ensures seamless data sharing and coordination between different departments, such as operations and maintenance.
Set Up AI Algorithms and Machine Learning Models
Once the IoT data is flowing into the system, AI algorithms and machine learning models are set up to analyse the data. Historical data is used to train these models, which then learn to recognize patterns and predict asset failures. As more data is collected, the AI models improve in accuracy over time.
Create a Centralised Dashboard and Reporting Mechanisms
The APM software should provide a centralised dashboard where users can view real-time data, historical trends, and predictive insights. Alerts and notifications should be configured to inform maintenance teams of potential issues before they escalate.
In addition, the system should offer customizable reporting tools to generate insights on asset performance, maintenance activities, and cost savings.
Pilot and Test the System
Before rolling out the APM system organisation-wide, it is advisable to run a pilot program. Select a small subset of assets to test the software and ensure that it meets the intended goals, such as reducing downtime or improving asset reliability. Use the pilot phase to fine-tune the system and address any issues.
Scale the Implementation
Once the pilot is successful, the APM software can be scaled across the organisation to cover more assets and facilities. Continuous monitoring and optimization are essential to ensure the system delivers long-term value.
Employee Training and Change Management
Implementing AI and IoT-enabled APM software requires a cultural shift within the organisation. Employees, particularly those in operations and maintenance, must be trained on how to use the new system. Emphasise the value of data-driven decision-making and ensure that the workforce is comfortable using the tools provided by the APM platform.
Real-World Use Cases of AI and IoT-Enabled APM Software
AI and IoT-enabled APM software is being widely adopted across industries. Here are a few examples of its application in different sectors:
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing industry, predictive maintenance has proven to be a game-changer. AI-driven APM systems analyse machine data in real-time to predict when a piece of equipment is likely to fail. By addressing issues before they occur, manufacturers can avoid costly downtime and keep production lines running smoothly.
Oil and Gas
In the oil and gas industry, APM systems are used to monitor critical assets such as pipelines, drilling rigs, and refineries. By leveraging IoT sensors and AI algorithms, companies can detect potential leaks or equipment malfunctions early, preventing environmental hazards and reducing maintenance costs.
Energy and Utilities
Energy companies use AI and IoT-enabled APM software to monitor the performance of turbines, generators, and power grids. By optimising asset performance, these companies can reduce energy consumption, extend the lifespan of equipment, and improve overall grid reliability.
Transportation and Logistics
In transportation, APM systems are used to track the health of vehicles, trains, and aircraft. By predicting when components such as engines or brakes need maintenance, companies can reduce downtime and ensure safe, reliable operations.
Challenges and Considerations
While AI and IoT-enabled APM software offers significant benefits, there are also challenges to consider:
Challenges
• Data Security:
The vast amounts of data collected by IoT sensors need to be securely managed to prevent cyber threats.
• Initial Investment:
The upfront costs of implementing IoT sensors and AI software can be substantial. However, the long-term financial benefits typically outweigh the initial expenses.
• Integration Complexity:
Integrating APM systems with existing software platforms and workflows can be complex, requiring robust planning and execution.
Considerations
• Data Quality and Management:
Ensuring high-quality, reliable data is essential for accurate insights and effective decision-making in APM systems.
• User Training and Adoption:
Providing adequate training for staff on new APM technologies is crucial for successful implementation and to maximize the benefits of the system.
• Cost of Implementation:
Assessing the total cost of ownership, including initial setup, ongoing maintenance, and potential upgrades, is vital for making informed investment decisions in APM solutions.
Conclusion
AI and IoT-enabled APM software revolutionizes asset management by leveraging real-time data and analytics to optimize performance, cut maintenance costs, and extend asset lifespans. With predictive and prescriptive maintenance, businesses minimize downtime, improve resource allocation, and maximize ROI. As industries embrace digital transformation, APM software enhances efficiency, sustainability, and competitiveness across manufacturing, oil and gas, energy, and transportation.





